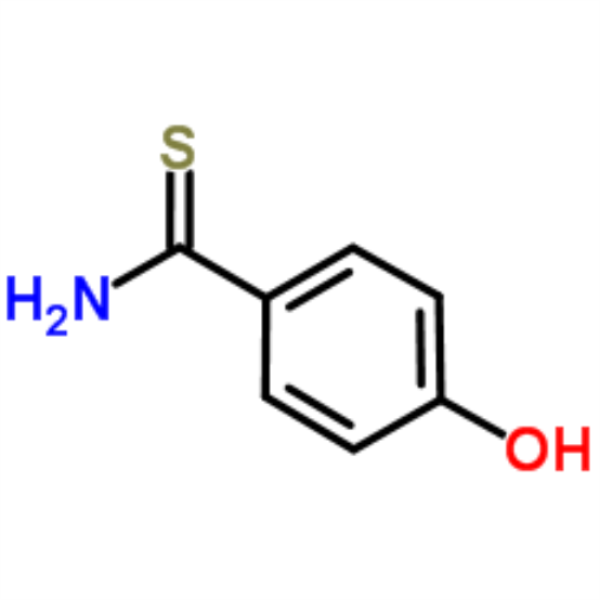
4-Hydroxythiobenzamide CAS 25984-63-8 Purity >99.0% (HPLC) Febuxostat Intermediate Factory
Ruifu Chemical Supply Febuxostat Related Intermediates:
Febuxostat CAS 144060-53-7
Ethyl 2-Chloroacetoacetate CAS 609-15-4
4-Hydroxythiobenzamide CAS 25984-63-8
Ethyl 2-(3-Cyano-4-Hydroxyphenyl)-4-Methyl-1,3-Thiazole-5-Carboxylate CAS 161798-02-3
Ethyl 2-(3-Cyano-4-Isobutoxyphenyl)-4-Methyl-5-Thiazolecarboxylate CAS 160844-75-7
Ethyl 2-(3-Formyl-4-Hydroxyphenyl)-4-Methylthiazole-5-Carboxylate CAS 161798-01-2
Ethyl 2-(3-Formyl-4-Isobutoxyphenyl)-4-Methylthiazole-5-Carboxylate CAS 161798-03-4
Ethyl 2-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-4-Methylthiazole-5-Carboxylate CAS 161797-99-5
| Chemical Name | 4-Hydroxythiobenzamide |
| Synonyms | p-Hydroxythiobenzamide; 4-Hydroxy-thiobenzamide; p-Hydroxythio-benzamide; 4-Hydroxybenzenecarbothioamide; 4-Hydroxybenzothioamide |
| CAS Number | 25984-63-8 |
| CAT Number | RF-PI1855 |
| Stock Status | In Stock, Production Scale Up to Tons |
| Molecular Formula | C7H7NOS |
| Molecular Weight | 153.20 |
| Melting Point | 181.0~185.0℃ |
| Density | 1.338±0.06 g/cm3 |
| Solubility (Soluble in) | Soluble in Methanol |
| Brand | Ruifu Chemical |
| Item | Specifications |
| Appearance | Pale Yellow Solid Powder |
| Purity / Analysis Method | >99.0% (HPLC) |
| Identification | By HPLC; By HNMR |
| Loss on Drying | <0.50% |
| Residue on Ignition | <0.20% |
| Single Impurity | <0.50% |
| Total Impurities | <1.00% |
| Test Standard | Enterprise Standard |
| Usage | Intermediate of Febuxostat (CAS: 144060-53-7) |
Package: Bottle, Aluminium foil bag, 25kg/Cardboard Drum, or according to customer's requirement
Storage Condition: Store in sealed containers at cool and dry place; Protect from light and moisture


4-Hydroxythiobenzamide (CAS: 25984-63-8) can be used as an intermediate of Febuxostat (CAS: 144060-53-7). Febuxostat, a selective xanthine oxidase inhibitor, was launched for the chronic management of hyperuricemia in patients with gout. Hyperuricemia is defined as a serum uric acid concentration exceeding the limit of solubility. It predisposes affected persons to gout, a disease characterized by the formation of crystals of monosodium urate or uric acid from supersaturated fluids in joints and other tissues.
-
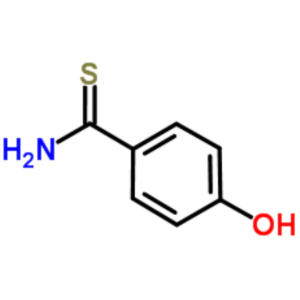
4-Hydroxythiobenzamide CAS 25984-63-8 Purity >9...
-
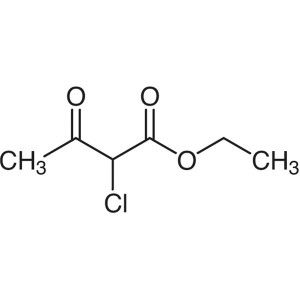
Ethyl 2-Chloroacetoacetate CAS 609-15-4 Purity ...
-
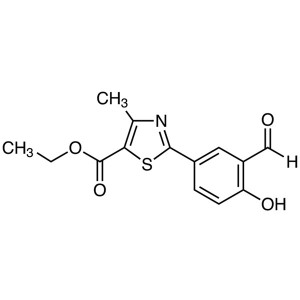
Ethyl 2-(3-Formyl-4-Hydroxyphenyl)-4-Methylthia...
-
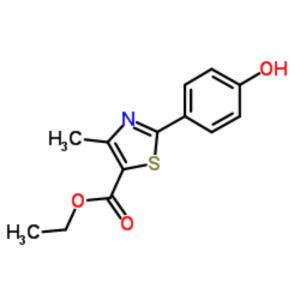
Ethyl 2-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-4-Methylthiazole-5-Ca...
-
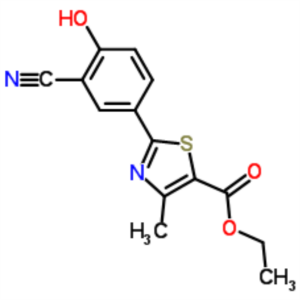
Febuxostat 4-Hydroxy Ethyl Ester CAS 161798-02-...
-
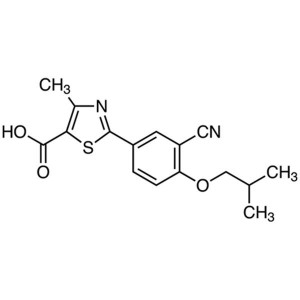
Febuxostat CAS 144060-53-7 Purity >99.0% (HPLC)...
-
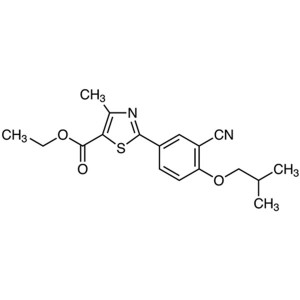
Febuxostat Ethyl Ester CAS 160844-75-7 Purity >...
-
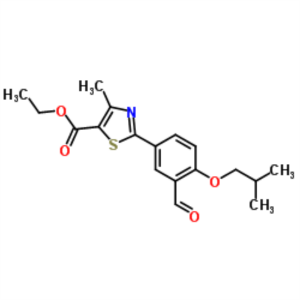
Febuxostat Formyl Hydroxy Ethyl Ester CAS 16179...