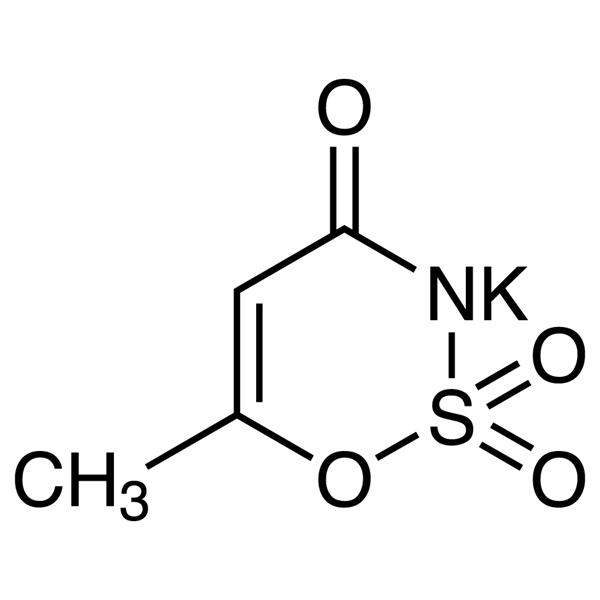
Acesulfame K CAS 55589-62-3 Acesulfame Potassium Purity >99.0% (HPLC)
Shanghai Ruifu Chemical Co., Ltd. is the leading manufacturer of Acesulfame K (Acesulfame Potassium) (CAS: 55589-62-3) with high quality, food ingredient sweetener. Ruifu can provide worldwide delivery, competitive price, small and bulk quantities available. Purchase Acesulfame K, Please contact: alvin@ruifuchem.com
| Chemical Name | Acesulfame K |
| Synonyms | Acesulfame Potassium; Acesulfame Potassium Salt; 6-Methyl-1,2,3-Oxathiazin-4(3H)-one 2,2-Dioxide Potassium Salt; Potassium 6-Methyl-1,2,3-Oxathiazin-4(3H)-one 2,2-Dioxide; Otizon; Potassium Acesulfame; Sunett; Sunnett; Sweet One; ADI |
| Stock Status | In Stock, Commercially Manufactured |
| CAS Number | 55589-62-3 |
| Molecular Formula | C4H4KNO4S |
| Molecular Weight | 201.24 g/mol |
| Melting Point | 229.0~232.0℃(dec.) |
| Sensitive | Moisture Sensitive |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in Water, Almost Transparency |
| Odor | Odorless with Sweet Taste |
| Storage Temp. | Cool & Dry Place (2~8℃, Away From Moisture) |
| COA & MSDS | Available |
| Brand | Ruifu Chemical |
| Items | Inspection Standards | Results |
| Appearance | White Crystalline Powder | Complies |
| Assay Content | 99.0~101.0% (Calculated on the Dried Basis) | 99.63% |
| Melting Point | 229.0~232.0℃ | Complies |
| Loss on Drying | <1.00% | 0.09% |
| Sulphate Ash | <0.50% | Complies |
| pH Value (1 in 100 Solution) | 5.5~7.5 | 6.65 |
| Potassium | 17.0~21.0% | Complies |
| Organic impurities | ≤20ppm | Complies |
| Impurity A | ≤0.125% | Complies |
| Impurity B | ≤20ppm | Complies |
| Heavy Metals (Pb) | ≤10ppm | <5ppm |
| Fluoride | ≤3ppm | Complies |
| Arsenic | ≤3ppm | Complies |
| Lead | ≤1ppm | Complies |
| Selenium | ≤10ppm | Complies |
| Infrared Spectrum | Conforms to Structure | Complies |
| 1 H NMR Spectrum | Conforms to Structure | Complies |
| Conclusion | The product has been tested & complies with the specifications | |
Package: Bottle, Aluminium foil bag, 25kg/Cardboard Drum, or according to customer's requirement.
Storage Condition: Store in a tightly closed container. Store in a cool, dry (2~8℃) and well-ventilated warehouse away from incompatible substances. Protect from light and moisture.
Shipping: Deliver to worldwide by air, by FedEx / DHL Express. Provide fast and reliable delivery.
DEFINITION
Acesulfame Potassium contains NLT 99.0% and NMT 101.0% of C4H4NO4SK, calculated on the dried basis.
IDENTIFICATION
• A. INFRARED ABSORPTION <197K>
• B. IDENTIFICATION TESTS-GENERAL, Potassium <191>
Sample solution: 100 mg/mL
Acceptance criteria: Meets the requirements
ASSAY
• PROCEDURE
Sample: 150 mg
Titrimetric system (See Titrimetry <541>)
Mode: Direct titration
Titrant: 0.1 N perchloric acid VS
Blank: 50 mL of glacial acetic acid
Endpoint detection: Potentiometric
Analysis: Dissolve the Sample in 50 mL of glacial acetic acid.
Titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS. Perform a blank determination.
Calculate the percentage of acesulfame potassium (C4H4NO4SK) in the Sample:
Result = [(V − B) × N × F × 100]/W
V = titrant volume consumed by the Sample (mL)
B = titrant volume consumed by the Blank (mL)
N = titrant actual normality (mEq/mL)
F = equivalency factor, 201.2 mg/mEq
W = weight of Sample (mg)
Acceptance criteria: 99.0%–101.0% on the dried basis
IMPURITIES
• LIMIT OF FLUORIDE
[NOTE-Use plasticware throughout this test.]
Solution A: Dissolve 210 g of citric acid monohydrate in 400 mL of water. Adjust with concentrated ammonia to a pH of 7.0, and dilute with water to 1000 mL.
Solution B: 132 mg/mL of dibasic ammonium phosphate
Solution C: To a suspension of 292 g of edetic acid in 500 mL of water, add 200 mL of ammonium hydroxide, adjust with ammonium hydroxide to a pH between 6 and 7, and dilute with water to make 1000 mL.
Buffer solution: Mix equal volumes of Solution A, Solution B and Solution C, and adjust with ammonium hydroxide to a pH of 7.5.
Standard stock solution: Weigh 0.442 g of sodium fluoride, previously dried at 300° for 12 h, into a 1-L volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. Store the solution in a closed plastic container. Immediately before use, pipet 5 mL of this solution into a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. Each mL of this solution contains 10µg of fluoride ion.
Standard solution A: Mix 0.5 mL of Standard stock solution and 15.0 mL of Buffer solution, and dilute with water to 50mL.
Standard solution B: Mix 1.0 mL of Standard stock solution and 15.0 mL of Buffer solution, and dilute with water to 50mL.
Standard solution C: Mix 1.5 mL of Standard stock solution and 15.0 mL of Buffer solution, and dilute with water to 50mL.
Standard solution D: Mix 3.0 mL of Standard stock solution and 15.0 mL of Buffer solution, and dilute with water to 50mL.
Sample solution: To a 50-mL volumetric flask add 3 g of Acesulfame Potassium. Dissolve in water, add 15.0 mL of Buffer solution, and dilute with water to volume.
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution A, Standard solution B, Standard solution C, Standard solution D, and Sample solution
Concomitantly measure the potential (see Titrimetry <541>) in mV, of the Standard solutions and the Sample solution, with a suitable pH meter equipped with a fluoride-specificion electrode and a silver-silver chloride reference electrode. When taking the measurements, transfer the solution to a 25-mL beaker, and immerse the electrodes. Insert a polytef-coated stirring bar into the beaker, place the beaker on a magnetic stirrer having an insulated top and allow to stir until equilibrium is attained (1-2 min). Rinse, and dry the electrodes between measurements, taking care not to scratch the crystal in the fluoride-specific ion electrode. Measure the potential of each Standard solution, and plot the fluoride concentration, in µg/mL, versus the potential, in mV, on semilogarithmic paper. Measure the potential of the Sample solution, and determine the fluoride concentration from the standard curve, in µg/mL.
Calculate the content, in ppm, of fluoride in the portion of Acesulfame Potassium taken:
Result = (V × C/W)
V = volume of the Sample solution (mL)
C = concentration of fluoride in the Sample solution, from the standard curve (mg/mL)
W = weight of Acesulfame Potassium taken to prepare the Sample solution (g)
Acceptance criteria: NMT 3 ppm
• HEAVY METALS, Method I <231>: NMT 10 ppm
• CHROMATOGRAPHIC PURITY
Solution A: 3.3 mg/mL of tetrabutylammonium hydrogen sulfate
Mobile phase: Acetonitrile and Solution A (2:3)
System suitability solution: 2 µg/mL each of USP Acesulfame Potassium RS and ethylparaben
Standard solution: 0.2 µg/mL of USP Acesulfame Potassium RS
Sample solution: 10 mg/mL
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography <621>, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 227 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-µm packing L1
Flow rate: 1 mL/min
Injection size: 20 µL
System suitability
Sample: System suitability solution
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 2 between acesulfame potassium and ethylparaben
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Record the chromatograms for a run time NLT 3 times the retention time of the acesulfame potassium peak, and measure the area responses of the peaks.
Acceptance criteria: The response of any peak at a retention time other than that of acesulfame potassium from the Sample solution does not exceed the response of the acesulfame potassium peak from the Standard solution (0.002%).
SPECIFIC TESTS
• ACIDITY OR ALKALINITY
Sample solution: 4.0 g in 20 mL of carbon dioxide-free water
Analysis: Add 0.1 mL of bromothymol blue TS. If the solution is yellow, titrate with 0.01 N sodium hydroxide to produce a blue color. If the solution is blue, titrate with 0.01 N hydrochloride acid to produce a yellow color.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.2 mL of 0.01 N sodium hydroxide or NMT 0.2 mL of 0.01 N hydrochloric acid is required.
• LOSS ON DRYING <731>: Dry a sample at 105° for 3 h: it loses NMT 1.0% of its weight.
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• PACKAGING AND STORAGE: Preserve in a well-closed container, and protect from light. Store at room temperature.
USP REFERENCE STANDARDS <11>
USP Acesulfame Potassium RS
How to Purchase? Please contact Dr. Alvin Huang: sales@ruifuchem.com or alvin@ruifuchem.com
15 Years Experience? We have more than 15 years of experience in the manufacture and export of a wide range of high quality pharmaceutical intermediates or fine chemicals.
Main Markets? Sell to domestic market, North America, Europe, India, Korea, Japanese, Australia, etc.
Advantages? Superior quality, affordable price, professional services and technical support, fast delivery.
Quality Assurance? Strict quality control system. Professional equipment for analysis include NMR, LC-MS, GC, HPLC, ICP-MS, UV, IR, OR, K.F, ROI, LOD, MP, Clarity, Solubility, Microbial limit test, etc.
Samples? Most products provide free samples for quality evaluation, shipping cost should be paid by customers.
Factory Audit? Factory audit welcome. Please make an appointment in advance.
MOQ? No MOQ. Small order is acceptable.
Delivery Time? If within stock, three days delivery guaranteed.
Transportation? By Express (FedEx, DHL), by Air, by Sea.
Documents? After sales service: COA, MOA, ROS, MSDS, etc. can be provided.
Custom Synthesis? Can provide custom synthesis services to best fit your research needs.
Payment Terms? Proforma invoice will be sent first after confirmation of order, enclosed our bank information. Payment by T/T (Telex Transfer), PayPal, Western Union, etc.
Risk Codes 36/37/38 - Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin.
Safety Description
S26 - In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice.
S36/37/39 - Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection.
WGK Germany 1
RTECS RP4489165
HS Code 2934990002
Toxicity LD50 in rats (mg/kg): 7431 orally, 2243 i.p. (Mayer, Kemper)
1976, Acesulfame-K was first synthesized
1983, EU approved its use in food and beverage
1988, FDA approved its use in table sweetening agent, gum and coffee
1992, China approved its use in food and beverage
1994, FDA approved its use in syrup, bakery and dairy products
1995, FDA approved its use in alcoholic drink
1998, FDA approved its use in soft drinks
2000, Japan approved its use
Acesulfame K (Acesulfame Potassium) (CAS: 55589-62-3) is an artificial sweetener.
As non-nutritive sweeteners, there is essentially no change in the concentration of foods and beverages used in the general pH range.
Common applications of Acesulfame-K are table uses, chewing gums, beverages, foods, bakery products, confectionary, oral hygiene products, and pharmaceuticals.
Sweeteners. After ingestion of the human body is not absorbed, does not produce heat, suitable for use in patients with diabetes and obesity. It can be used alone or in combination with other sweeteners. Acesulfame K is often blended with other sweeteners (usually Sucralose or Aspartame). These blends are reputed to give a more sucrose like taste whereby each sweetener masks the other's aftertaste, and/or exhibits a synergistic effect by which the blend is sweeter than its components.
Unlike Aspartame, Acesulfame K is stable under heat, even under moderately acidic or basic conditions, allowing it to be used as a food additive in baking, or in products that require a long shelf life. In carbonated drinks, it is almost always used in conjunction with another sweetener, such as Aspartame or Sucralose. It is also used as a sweetener in protein shakes and pharmaceutical products, especially chewable and liquid medications, where it can make the active ingredients more palatable.
Acesulfame potassium is used as an intense sweetening agent in cosmetics, foods, beverage products, table-top sweeteners, vitamin and pharmaceutical preparations, including powder mixes, tablets, and liquid products. It is widely used as a sugar substitute in compounded formulations,and as a toothpaste sweetener. The approximate sweetening power is 180–200 times that of sucrose, similar to aspartame, about one-third as sweet as sucralose, one-half as sweet as sodium saccharin, and about 4-5 times sweeter than sodium cyclamate.It enhances flavor systems and can be used to mask some unpleasant taste characteristics.
Acesulfame Potassium is widely used in beverages, cosmetics, foods, and pharmaceutical formulations, and is generally regarded as a relatively nontoxic and nonirritant material. Pharmacokinetic studies have shown that acesulfame potassium is not metabolized and is rapidly excreted unchanged in the urine. Long-term feeding studies in rats and dogs showed no evidence to suggest acesulfame potassium is mutagenic or carcinogenic.
The WHO has set an acceptable daily intake for acesulfame potassium of up to 15 mg/kg body-weight.The Scientific Committee for Foods of the European Union has set a daily intake value of up to 9 mg/kg of body-weight.
LD50 (rat, IP): 2.2 g/kg
LD50 (rat, oral): 6.9–8.0 g/kg
Acesulfame Potassium possesses good stability. In the bulk form it shows no sign of decomposition at ambient temperature over many years. No reduction in sweetness was observed over a period of approximately 2 years. Stability at elevated temperatures is good, although some decomposition was noted following storage at 408℃ for several months. Sterilization and pasteurization do not affect the taste of acesulfame potassium.
The bulk material should be stored in a well-closed container in a cool, dry place and protected from light.
Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database for oral and sublingual preparations. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients. Accepted for use in Europe as a food additive. It is also accepted for use in certain food products in the USA and several countries in Central and South America, the Middle East, Africa, Asia, and Australia.