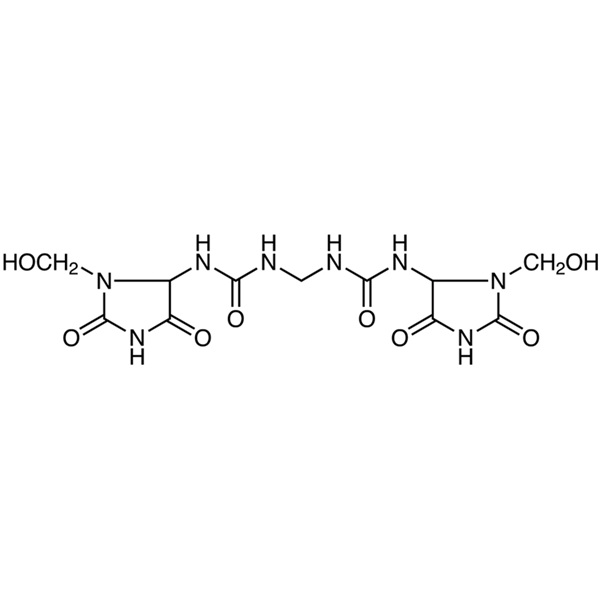
Imidazolidinyl Urea CAS 39236-46-9 Purity ≥98.0% Factory
Manufacturer Supply, High Purity, Commercial Production
Chemical Name: Imidazolidinyl Urea
CAS: 39236-46-9
| Chemical Name | Imidazolidinyl Urea |
| Synonyms | N,N'-Methylenebis[N'-(3-hydroxymethyl-2,5-dioxo-4-imidazolidinyl)urea]; Imidurea |
| CAS Number | 39236-46-9 |
| CAT Number | RF-F05 |
| Stock Status | In Stock, Production Scale Up to Tons |
| Molecular Formula | C11H16N8O8 |
| Molecular Weight | 388.30 |
| Melting Point | 141.0~143.0℃ |
| Solubility | Soluble in Water and Glycerol |
| Brand | Ruifu Chemical |
| Item | Specifications |
| Appearance | White Crystalline Powder |
| Purity | ≥98.0% |
| Total Impurities | ≤2.0% |
| Test Standard | Enterprise Standard |
| Usage | Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Preservative Used in Cosmetics |
Package: Bottle, Aluminium foil bag, 25kg/Cardboard Drum, or according to customer's requirement.
Storage Condition: Store in sealed containers at cool and dry place; Protect from light and moisture.


Imidazolidinyl Urea (CAS: 39236-46-9) is a broad-spectrum antimicrobial preservative used in cosmetics and topical pharmaceutical formulations; typical concentrations used are 0.03–0.5% w/w. It is effective between pH 3~9 and is reported to have synergistic effects when used with parabens. Imidazolidinyl urea, a formaldehyde releaser related to diazolidinyl urea, is used as an antimicrobial agent very active against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, used as a synergist in combination with para- bens. It is used as a preservative in aqueous products, mainly in cosmetics, toiletries, and liquid soaps. Imidazolidinyl Urea is incompatible with strong oxidants. It is compatible with other preservatives including sorbic acid and quaternary ammonium compounds. It is also compatible with other pharmaceutical and cosmetic excipients including proteins, nonionic surfactants, and lecithin. Can be used for cream, shampoo, dew, conditioner and other products, can be used alone, can also be used with paraben ester, IPBC and other products, enhance its anticorrosive effect.
-
Imidazolidinyl Urea CAS 39236-46-9 Purity ≥98.0...
-
Imidazole CAS 288-32-4 Purity ≥99.5% (GC) Facto...
-
Benzimidazole CAS 51-17-2 Purity ≥99.5% (HPLC) ...
-
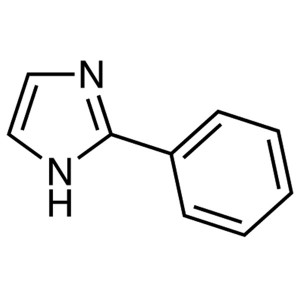
2-Phenylimidazole CAS 670-96-2 Purity >99.0% (G...
-
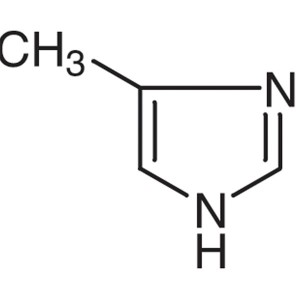
4-Methylimidazole CAS 822-36-6 Purity ≥99.5% (G...
-
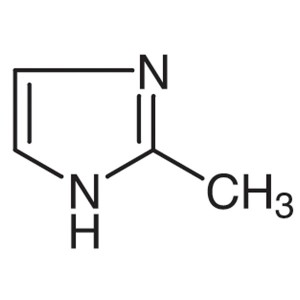
2-Methylimidazole CAS 693-98-1 Purity >99.5% (G...
-
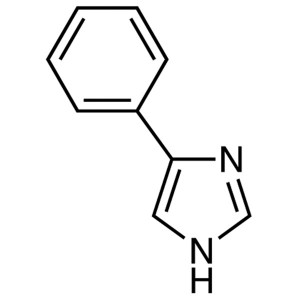
4-Phenylimidazole CAS 670-95-1 Purity ≥99.0% (H...
-
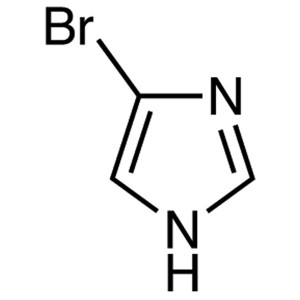
4-Bromoimidazole CAS 2302-25-2 Purity >99.0% (G...
-
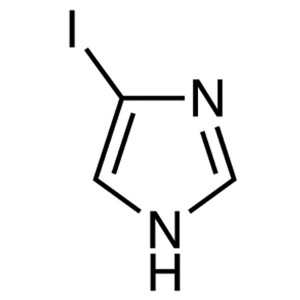
4-Iodoimidazole CAS 71759-89-2 Purity ≥99.5% (H...
-
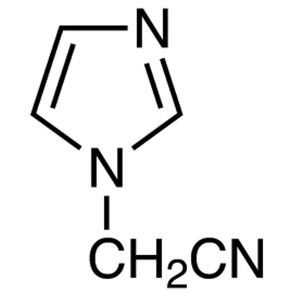
(1-Imidazolyl)acetonitrile CAS 98873-55-3 Lulic...
-
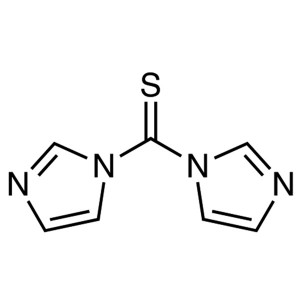
1,1′-Thiocarbonyldiimidazole (TCDI) CAS 6...
-
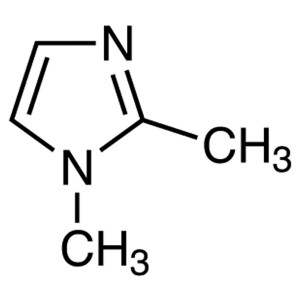
1,2-Dimethylimidazole CAS 1739-84-0 Purity >99....
-
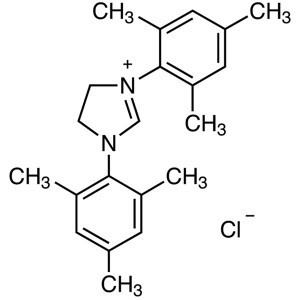
1,3-Bis(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)imidazolinium Chl...
-
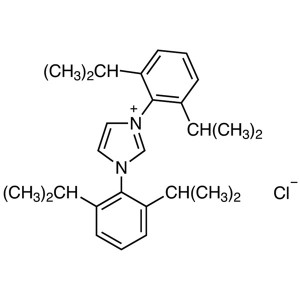
1,3-Bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)imidazolium Chlor...
-
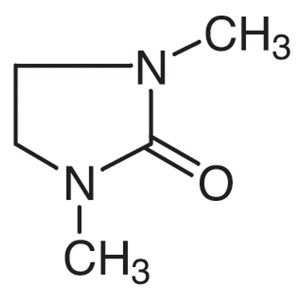
1,3-Dimethyl-2-Imidazolidinone CAS 80-73-9 (DMI...
-
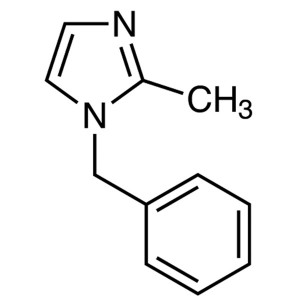
1-Benzyl-2-Methylimidazole CAS 13750-62-4 Assay...