L-Aspartic Acid CAS 56-84-8 (H-Asp-OH) Assay 98.5~101.0% Factory High Quality
Shanghai Ruifu Chemical Co., Ltd. is the leading manufacturer and supplier of L-Aspartic Acid (H-Asp-OH; L-Asp; Abbreviated Asp or D) (CAS: 56-84-8) with high quality, production capacity 5000 Tons per year. Ruifu Chemical supplys a series of amino acids derivatives. We can provide worldwide delivery, competitive price, small and bulk quantities available. If you are interested in L-Aspartic Acid, Please contact: alvin@ruifuchem.com
| Chemical Name | L-Aspartic Acid |
| Synonyms | H-Asp-OH; L-(+)-Aspartic Acid; L-Asp; Abbreviated Asp or D; Aspartic Acid; Laevo-Aspartic Acid; (S)-Aminosuccinic Acid; L-Asparaginic Acid; (S)-Aminobutanedioic Acid; L-2-Aminobutanedioic Acid; L-Aminosuccinic Acid |
| Stock Status | In Stock, Production Capacity 5000 Tons per Year |
| CAS Number | 56-84-8 |
| Molecular Formula | C4H7NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 133.10 |
| Melting Point | >300℃(dec.)(lit.) |
| Density | 1.66 |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble in Water, 5 g/L 25℃ |
| Solubility | Practically Insoluble in Ethanol and in Ether. Dissolves in Dilute Hydrochloric Acid and in Dilute Nitric Acid |
| Solubility in HCl (1+10) | Almost Transparency |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible With Strong Oxidising Agents |
| Storage Temp. | Sealed in Dry, Store at Room Temperature |
| COA & MSDS | Available |
| Classification | Amino Acid and Derivatives |
| Brand | Ruifu Chemical |
| Hazard Codes | Xi,Xn | RTECS | CI9098500 |
| Risk Statements | 36-36/37/38-20/21/22 | F | 10 |
| Safety Statements | 26-24/25-22-36 | TSCA | Yes |
| WGK Germany | 2 | HS Code | 2922491990 |
| Hazard Class | Irritant |
| Items | Inspection Standards | Results |
| Appearance | White Crystals or Crystalline Powder, Acid Taste | Conforms |
| Identification | Infrared Absorption | Conforms |
| Specific Rotation [α]20/D | +24.80° to +25.80° (C=8, 6mol/L HCl) |
+25.10° |
| State of Solution | ≥98.0% (Transmittance) | 98.5% |
| Chloride (Cl) | ≤0.020% | <0.020% |
| Sulfate (SO4) | ≤0.020% | <0.020% |
| Ammonium (NH4) | ≤0.020% | <0.020% |
| Iron (Fe) | ≤10ppm | <10ppm |
| Heavy Metals (Pb) | ≤10ppm | <10ppm |
| Arsenic (As2O3) | ≤1.0ppm | <1.0ppm |
| Other Amino Acids | Chromatographically Not Detectable |
Conforms |
| Loss on Drying | ≤0.20% (at 105℃ for 3 Hours) | 0.16% |
| Residue on Ignition | ≤0.10% | 0.08% |
| Assay | 98.5~101.0% (Titration: Anhydrous Basis) | 99.7% |
| pH Test | 2.5 to 3.5 | 2.9 |
| Conclusion | Accords with the Standard of AJI97; JP | |
| Shelf Life | 24 Months From Manufacture Date if Stored Properly | |
Package: Fluorinated Bottle, 25kg/bag, 25kg/Cardboard Drum, or according to customer's requirement.
Storage Condition: Store in sealed containers at cool, dry and ventilated warehouse away from incompatible substances. Protect from light and moisture.
L-Aspartic Acid, when dried, contains not less than 98.5% and not more than 101.0% of L-Aspartic Acid (C4H7NO4).
Description L-Aspartic Acid occurs as white, crystals orcrystalline powder. It is sparingly soluble in water, and practically insoluble in ethanol (99.5). It dissolves in dilute hydrochloric acid and in 0.2 mol/L sodium hydroxide TS.
Identification Determine the infrared absorption spectrum of L-Aspartic Acid as directed in the potassium bromide disk method under Infrared Spectrophotometry <2.25>, and compare the spectrum with the Reference Spectrum: both spectraexhibit similar intensities of absorption at the same wave numbers.
Optical rotation <2.49> [a]20D: +24.0~+26.0° (2 g, after drying, 6 mol/L hydrochloric acid TS, 25 mL, 100 mm).
pH <2.54> Dissolve 0.4 g of L-Aspartic Acid in 100 mL of water by warming, and allow to cool: between 2.5 and 3.5.
Purity (1) Clarity and color of solution-Dissolve 1.0 g of L-Aspartic Acid in 20 mL of 1 mol/L hydrochloric acid TS: the solution is clear and colorless.
(2) Chloride <1.03>-Dissolve 0.5 g of L-Aspartic Acid in 6 mL of dilute nitric acid and 20 mL of water, add water to make 50 mL, and perform the test with this solution as the test solution. Prepare the control solution with 0.30 mL of 0.01 mol/L hydrochloric acid VS (not more than 0.021%).
(3) Sulfate <1.14>-Dissolve 0.6 g of L-Aspartic Acid in5 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid and 30 mL of water, add water to make 45 mL, and add 5 mL of barium chloride TS. Perform the test with this solution as the test solution. Pre-pare the control solution with 0.35 mL of 0.005 mol/L sulfuric acid VS, add 5 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid and water to make 45 mL, and add 5 mL of barium chloride (not more than 0.028~).
(4) Ammonium<1.02>—Perform the test with 0.25 g of L-Aspartic Acid. Prepare the control solution with 5.0 mL of Standard Ammonium Solution (not more than 0.02z)
(5) Heavy Metals <1.07>-Proceed with 1.0 g of L-Aspartic Acid according to Method 4, and perform the test. Prepare the control solution with 1.0 mL of Standard Lead Solution (not more than 10 ppm).
(6)Iron <1.10>-Prepare the test solution with 1.0 g of L-Aspartic Acid according to Method 1, and perform the testaccording to Method A. Prepare the control solution with1.0 mL of Standard Iron Solution (not more than 10 ppm).
(7) Related Substances-Dissolve 0.20 g of L-AsparticAcid in 10 mL of 0.2 mol/L sodium hydroxide TS, and usethis solution as the sample solution. Pipet 1 mL of the sample solution, add water to make exactly 10 mL. Pipet 1 mLof this solution, add water to make exactly 50 mL, and use this solution as the standard solution. Perform the test with these solutions as directed under Thin-layer Chromatogra-phy<2.03>. Spot 5mL each of the sample solution and stand-ard solution on a plate of silica gel for thin-layer chromatog-raphy, develop with a mixture of 1-butanol, water and aceticacid (100) (3:1:1) to a distance of about 10 cm, and dry theplate at 809C for 30 minutes. Spray evenly a solution of nin-hydrin in a mixture of methanol and acetic acid (100) (97:3)(1 in 100), and heat at 80℃ for 10 minutes: the spot other than the principal spot obtained with the sample solution isnot more intense than the spot obtained with the standard solution.
Loss on Drying <2.41> Not more than 0.30% (1 g, 105℃,3 hours).
Residue on Ignition <2.44> Not more than 0.1% (1 g).
Assay Weigh accurately about 0.15 g of L-Aspartic Acid, previously dried, dissolve in 50 mL of water by warming. After cooling, titrate <2.50> with 0.1 mo/L sodium hydroxide VS (potentiometric titration). Perform a blank determination in the same manner, and make any necessary correction.
Each mL of 0.1 mol/L sodium hydroxide VS=13.31 mg of C4H7NO4
Containers and storage Containers-Tight containers.
How to Purchase? Please contact Dr. Alvin Huang: sales@ruifuchem.com or alvin@ruifuchem.com
15 Years Experience? We have more than 15 years of experience in the manufacture and export of a wide range of high quality pharmaceutical intermediates or fine chemicals.
Main Markets? Sell to domestic market, North America, Europe, India, Korea, Japanese, Australia, etc.
Advantages? Superior quality, affordable price, professional services and technical support, fast delivery.
Quality Assurance? Strict quality control system. Professional equipment for analysis include NMR, LC-MS, GC, HPLC, ICP-MS, UV, IR, OR, K.F, ROI, LOD, MP, Clarity, Solubility, Microbial limit test, etc.
Samples? Most products provide free samples for quality evaluation, shipping cost should be paid by customers.
Factory Audit? Factory audit welcome. Please make an appointment in advance.
MOQ? No MOQ. Small order is acceptable.
Delivery Time? If within stock, three days delivery guaranteed.
Transportation? By Express (FedEx, DHL), by Air, by Sea.
Documents? After sales service: COA, MOA, ROS, MSDS, etc. can be provided.
Custom Synthesis? Can provide custom synthesis services to best fit your research needs.
Payment Terms? Proforma invoice will be sent first after confirmation of order, enclosed our bank information. Payment by T/T (Telex Transfer), PayPal, Western Union, etc.
Risk Codes R36 - Irritating to the eyes
R36/37/38 - Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin.
R20/21/22 - Harmful by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed.
Safety Description S26 - In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice.
S24/25 - Avoid contact with skin and eyes.
S22 - Do not breathe dust.
S36 - Wear suitable protective clothing.
WGK Germany 2
RTECS CI9098500
FLUKA BRAND F CODES 10
TSCA Yes
HS Code 2922491990
Hazard Class IRRITANT
Toxicity LD50 intraperitoneal in mouse: 6gm/kg
L-Aspartic Acid (H-Asp-OH) (CAS: 56-84-8) is mainly produced by enzymatic method. L-Aspartase acts on the fumaric acid and ammonia, that is, which generates L-Aspartic Acid. L-Aspartic Acid is the L-form of the aspartic acid. L-Aspartic Acid is one of the 20 amino acids that used in the protein synthesis. It is the non-essential amino acids for humans as it can be synthesized in vivo. It is important in the synthesis of other amino acids and some nucleotides, and is a metabolite in the citric acid and urea cycles. Currently, almost all the aspartic acids are manufactured in China.
Function and Application of L-Aspartic Acid CAS 56-84-8
1. L-Aspartic Acid is used as a component of parenteral and enteral nutrition and as a pharmaceutical ingredient. it is used for cell culture and in manufacturing processes. It is widely utilized for mineral supplementation in the salt form.
2. L-Aspartic Acid is used as a dietary supplement, it can be blended with minerals to make compounds like potassium aspartate, copper aspartate, manganese aspartate, magnesium aspartate, zinc aspartate and more. Increasing the absorption, and hence utilization potentials, of these minerals via the addition of aspartate induces certain health benefits. Many athletes use L-aspartic acid-based mineral supplements orally to enhance their performance capacities. Aspartic acid and glutamic acid play important roles as general acids in enzyme active centers, as well as in maintaining the solubility and ionic character of proteins. It can help promote a robust metabolism, and is sometimes used to treat fatigue and depression. Aspartic acid is used as a component of parenteral and enteral nutrition. In pharmaceutical agents aspartic acid is used as an ammoniac detoxicating agent, hepar function accelerator and fatigue refresher.
3. L-Aspartic Acid is an amino acid used as a skin-conditioning agent.
4. L-Aspartic Acid is widely used on medicine, food and chemical industry.
5. L-Aspartic Acid can be used on the treatment of heart disease, liver disease and hypertension.It has the function of preventing and recorving fatigue. It can be made of amino acid infusion to do as ammoniate antidote, liver function promoter and fatigue recovery agent.
6. L-Aspartic Acid can be used on tech industry. It is a good nutrition supplements that can be added in soft drinks. It is also the raw material of radix asparagi acyl methyl phenylalanine which is we know as Aspartame.
7. L-Aspartic Acid can be used on chemical industry. It is the raw material of synthetic resin.
8. L-Aspartic Acid can also be used as nutritive additive on cosmetics.
Aspartic Acid is widely used on medicine, food and chemical industry.
Aspartic Acid (abbreviatedas D-AA, Asp, or D) is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HOOCCH(NH2)CH2COOH. The carboxylate anion and salts of aspartic acid are knownas aspartate.
-
H-Asp(OBzl)-OBzl·TosOH CAS 2886-33-1 Purity >99...
-
N-Acetyl-D-Tryptophan CAS 2280-01-5 (Ac-D-Trp-O...
-
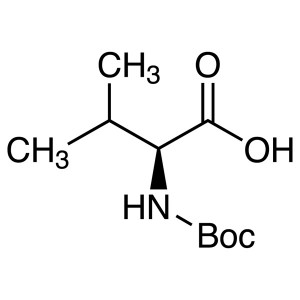
Boc-L-Valine CAS 13734-41-3 (Boc-Val-OH) Assay ...
-
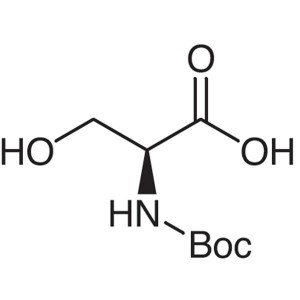
Boc-Ser-OH CAS 3262-72-4 (N-Boc-L-Serine) Purit...
-
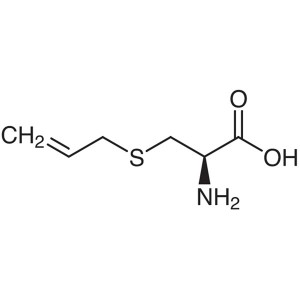
S-Allyl-L-Cysteine CAS 21593-77-1 Assay ≥98.0% ...
-
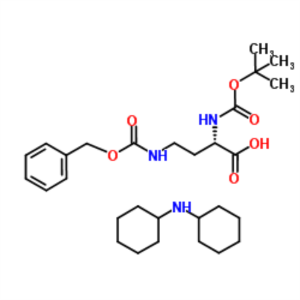
Boc-Dab(Z)-OH·DCHA CAS 16947-89-0 Purity >99.0%...